

SERVQUAL Model of Service Quality: this article describes the concept of the SERVQUAL Model of Service Quality by Valarie Zeithaml, A. Parasuraman and Leonard Berry in a practical way. Next to what it this framework is, this article also highlights it’s shortcomings, the dimensions, the five gaps of the SERVQUAL Model of Service Quality. Enjoy reading!
The Service Quality Model or SERVQUAL Model of Service Quality was developed and implemented by the American marketing gurus Valarie Zeithaml, A. Parasuraman and Leonard Berry in 1988. It is a method to capture and measure the service quality experienced by customers.
Initially, emphasis was on the development of quality systems in the field product quality. Over time, it became more and more important to improve the quality of related services. Improved service quality could give organisations a competitive edge.

In addition, service in general became more important, and as a result, the SERVQUAL Model had a serious impact in the eighties. Back then, measuring service was abstract and not easily quantifiable.
The SERVQUAL Model of Service Quality is primarily a qualitative analysis. If a satisfaction survey mainly depends on the transactions between supplier and buyer, the observed quality is measured through generic, environmental factors.
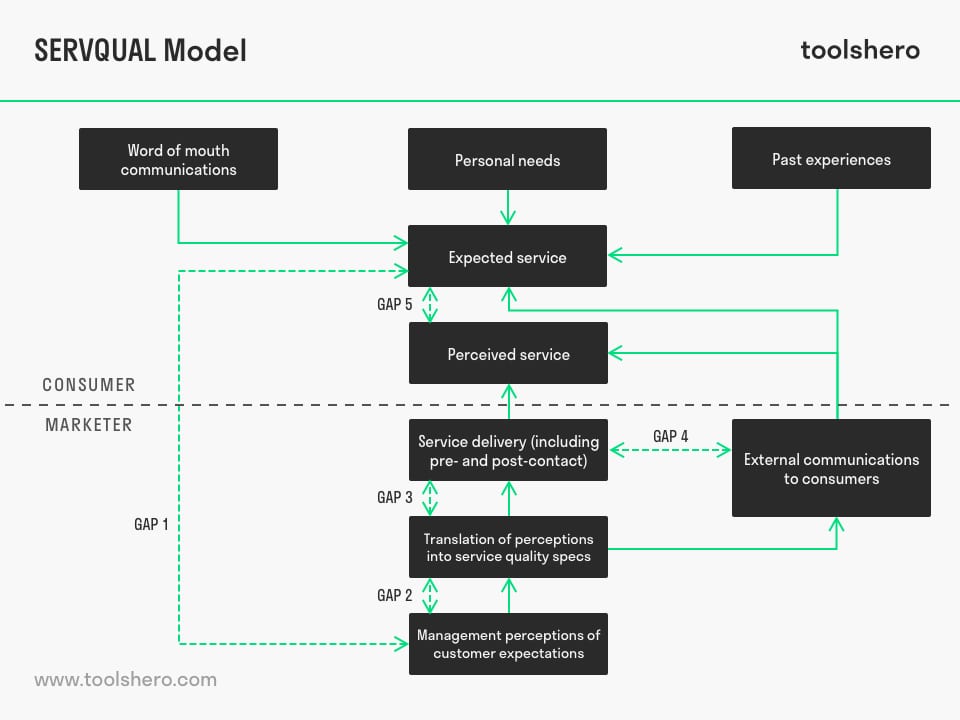
Figure 1 – SERVQUAL Model of Service Quality Diagram
This framework can be used to expose shortcomings in the service and address them. In that sense, it is a so-called ‘GAP Analysis‘. It compares the expected service quality and the service quality that has actually been experienced.
This experience is measured based on the customers perceptions. It is an external analysis of customer needs in relation to the quality of the service they experienced. Because of that, the focus is always on customer needs and not on the measuring system or the organisation’s perception; the way they would like to see themselves.
Furthermore, when determining the customer needs, the gap between customer expectations and the actual service they experience, needs to be taken into account.
Central to the SERVQUAL Model of Service Quality is the expectancy pattern of the service quality; the difference between expectations and perception. It there is a difference in quality, that is shown in the difference (the gap) between what was expected and what was actually experienced.
The SERVQUAL Model enables organisations to learn which factors play a role how the customer’s expectancy pattern is formed. That way, the organisation can improve itself and take this expectancy pattern into account beforehand.
The first studies according to the SERVQUAL Model of Service Quality, were carried out exclusively for the services of a telecommunications, a banking and a maintenance company. The previously mentioned researched surveyed consumers and their perceptions of the experienced service quality of these three organisations.
From the original questionnaire of almost 100 items, 25 finally remained that were considered important by the consumers regarding customer service. In the end, this resulted in the following ten dimensions that still play an important role in the SERVQUAL Model:
The reliability depends on to what extent the service is accurate and honest. Responsiveness is about promptly and adequately responding to customer questions or complaints. Competence relates to the expertise an organisation has and the access determines if a customer can quickly and efficiently contact the right department.
Courtesy is the trying to be polite to customers and communication is about clear, honest and prompt information for clients. Credibility is about to what extent the organisation’s message is believable and reliable.
Security is meant to add trust to the service and proper access for the consumer. Knowing the customer includes a personal approach and responding well to customers’ needs and wishes. The tangibles are tangible information; that what is visible to the customers in the form of for instance the visibility of staff (work clothes / uniform), the decoration and cleanliness of an office building and all other facilities.
A smaller version of the SERVQUAL Model of Service Quality is the RATER model. Where the SERVQUAL Model of Service Quality works with 10 dimensions to measure the quality of service, the RATER model works with 5 dimensions.
Both the communication between the customer and the service-providing organisation, as well as the organisation’s internal communication, are of vital importance for the level of quality of the service. It is good when organisations know the expectancy pattern of their customers.
Therefore, the SERVQUAL Model of Service Quality identifies five gaps that can arise between the customer’s needs and the service that a company offers.
A gap arises when an organisation’s knowledge of customer expectations is lacking, preventing them from approaching consumers in the right way.
The organisation has already formed its own idea about what the customer expects from their service. If this idea is wrong from the start and does not correspond to what customers actually expect, there is a significant risk that the organisation will translate it wrongly into a quality policy and corresponding rules.
A gap can also occur when the organisation offers service that is different from what the consumer had expected. This also involves an incorrect implementation. For instance, in the way employees carry out policy.
Sometimes, the external (marketing) communication that the organisation sends out, can create the wrong expectations among customers. It also happens that the organisation communicates and promises things that are not in line with what they can actually deliver.
Dissatisfaction results from a (significant) difference between the service a customer expects and the service they actually experience. Eventually, this will lead to the biggest gap in the experience of quality.

What do you think? What is your experience with the SERVQUAL Model of Service Quality? Do you recognize the practical explanation or do you have more additions? What are your success factors for good quality management?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
How to cite this article:
Mulder, P. (2018). SERVQUAL Model of Service Quality. Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/quality-management/servqual-model/
Original publication date: 01/17/2018 | Last update: 09/03/2024
Did you find this article interesting?
Your rating is more than welcome or share this article via Social media!
Average rating 4.6 / 5. Vote count: 23
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?